n premodern times, the theory of foreign relations of China held that the Chinese Empire was the Celestial Dynasty, the center of world civilization, with the Emperor of China being the leader of the civilized world. This view saw China as equivalent to "all under heaven". All other states were considered to be tributaries, under the suzerain rule of China. Some were direct vassals. Theoretically, the lands around the imperial capital were regarded as "five zones of submission", - the circular areas differentiated according to the strength of the benevolent influence from the Son of Heaven.
There were several periods when Chinese foreign policy took on isolationist tones, because of the view that the rest of the world was poor and backward with little to offer.
Nevertheless, China was a center of trade from early on in its history. Many of China's interactions with the outside world came via the Silk Road. This included, during the 2nd century AD, contact with representatives of the Roman Empire, and during the 13th century, the visits of Venetian traveler Marco Polo.
Chinese foreign policy was usually aimed at containing the threat of so-called "barbarian" invaders (such as the Xiongnu, Mongols, and Jurchen) from the north. This could be done by military means, such as an active offense (campaigns into the north) or a more passive defense (as exemplified by the Great Wall of China). The Chinese also arranged marriage alliances known as heqin, or "peace marriages."
Chinese officers distinguished between "matured/familiar barbarians" (foreigners influenced by Chinese culture) and "raw barbarians".[citation needed]
In many periods, Chinese foreign policy was especially assertive. One such case was exemplified by the treasure voyages of Admiral Zheng He during the Ming dynasty.
lthough many kings of the Shang and Zhou dynasties ruled beforehand, in 221 BC, the ruler of the Qin state, Ying Zheng (Qin Shi Huang), was the first to conquer the different vassal states under the Zhou dynasty, as well as other non-sinicized states. He was able to transform these different states into a relatively unified and uniform empire, the Qin Empire. Under his leadership and a society modelled around strict adherence to legalist philosophy, his once backwater western frontier state conquered all of the rivaling Warring States in ancient China. The Chinese domain was also extended into Inner Mongolia and Manchuria to the north, and with naval expeditions sent to the south, the indigenous Baiyue of modern-day Guangdong and northern Vietnam (the latter called Jiaozhi, and then Annam during the Tang dynasty) were also quelled and brought under Chinese rule.
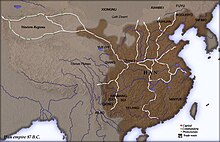
The time of the Han dynasty (202 BC–AD 220) was a groundbreaking era in the history of Imperial China's foreign relations, during the long reign of Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141–87 BC), the travels of the diplomat Zhang Qian opened up China's relations with many different Asian territories for the first time. While traveling to the Western Regions in order to seek out an alliance with the Yuezhi against the Xiongnu, Zhang Qian was imprisoned by the Xiongnu for many years, but he brought back detailed reports of lands that had been previously unknown to the Chinese. This included details of his travels to the Greek-Hellenized kingdoms of Fergana (Dayuan) and the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom (Daxia), as well as reports of Anxi (Persian Empire of Parthia), Tiaozhi (Mesopotamia), Shendu (India), and the Wusun Central Asian nomads. After his travels, the famous land trading route of the Silk Road leading from China to the Roman Empire was established. Emperor Wu was also known for his conquests and successful campaigns against the Xiongnu. He warred against the Kingdom of Wiman Joseon in order to establish the Four Commanderies of Han in Manchuria, one of which was established in northern Korea, the Lelang Commandery. The empire began expanding into southern China and northern Vietnam, then the territory of the Baiyue kingdoms. The Han Empire absorbed Minyue after defeating the state, and annexed the Dian in Yunnan. By 111 BC, Emperor Wu conquered the Nanyue kingdom in the Han–Nanyue War. Nanyue was ruled by the Triệu dynasty since the Qin naval officer Zhao Tuo had broken ties with mainland rule in the fall of Qin and establishment of Han.[1][2]
The Han dynasty in 87 BC, after the territorial expansion and establishment of the Silk Road during the reign of Emperor Wu.
he Han general Ban Chao (AD 32-102) reconquered the states in the Western Regions (the modern day Tarim Basin in Xinjiang) after pushing the Xiongnu out of the region. This included the kingdoms of Kashgar, Loulan, and Khotan, which were returned to Chinese control. He also sent his emissary Gan Ying even further in order to reach Rome (Daqin). Gan Ying perhaps made it as far as the Black Sea and Roman-era Syria, but turned back. He did however bring back reports of the Roman Empire, and there is evidence that subsequent Roman embassies to China took place.
The first diplomatic contact between China and the West occurred with the expansion of the Roman Empire in the Middle-East during the 2nd century, the Romans gained the capability to develop shipping and trade in the Indian Ocean. The first group of people claiming to be an embassy of Romans to China is recorded in 166, sixty years after the expeditions to the west of the Chinese general Ban Chao. It came to Emperor Huan of Han China, "from Antun (Emperor Antoninus Pius), king of Daqin (Rome)". Although, as Antoninus Pius died in 161, leaving the empire to his adoptive son Marcus Aurelius (Antoninus), the convoy arrived in 166, and the both Emperor being "Antonius" the confusion arises about who sent the embassy.
No comments:
Post a Comment